In this study, in order to detect gentamicin residues in animal tissues, monoclonal antibodies (Mab) were prepared and a sensitive indirect competitive chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay (icCLEIA) was established. First, gentamicin was combined with bovine serum albumin as an immunogen to immunize BALB/c mice. Then hybridoma technology was used to prepare anti-gentamicin monoclonal antibodies. Finally, an icCLEIA with a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 0.067 ng/mL against gentamicin was established. The detection limit of icCLEIA is 0.002 ng/mL. Cross-reactivity of mAbs with structural analogs <0.01%. The recovery rate of gentamicin in pork and fish samples was 80 ~ 101%, and the coefficient of variation was <6.4%. Samples were tested using UPLC-MS/MS to evaluate the reliability of icCLEIA. The results show that the prepared anti-gentamicin monoclonal antibody can be used for rapid and convenient immunological detection of gentamicin residues in animal tissues.
[Content introduction]
1. Preparation of antigen
Using carbodiimide coupling method to synthesize the carrier protein (BSA or OVA) Dissolve 10 mg in 2 ml PBS (0.01 M, pH 7.4), then add EDC (6 mg) and NHS (10 mg), stir gently at 25°C for 0.5 h, and then add gentamicin dissolved in 1 ml PBS. (10 mg) was dropped into the above solution. Stir for 3 hours at 25°C and dialyze against 0.01 M PBS (pH 7.4) for 3 days. The solution was then aliquoted and stored at -20°C; BSA-gentamicin conjugate was used for immunization and OVA-gentamicin coated antigen. Finally, the two conjugates were characterized using gold immunochromatography (GICA) to determine whether gentamicin was successfully conjugated to BSA and OVA carrier proteins.
2. Preparation of gentamicin monoclonal antibody
During the first immunization, emulsified BSA-gentamicin in FCA, 7 8-week-old BALB/c Female mice (per mouse) were immunized subcutaneously at multiple points with a dose of 150 µg. After 4 weeks, mice were injected with 50 µg of BSA-gentamicin in emulsion every 3 weeks until the 5th immunization. Seven days after the third boosted immunization, antiserum was obtained by drawing blood from the tail of the mice. Antibody titers of antisera were tested by indirect ELISA, and antibody selectivity was tested by indirect competitive ELISA. After the fourth immunization, mice with high serum dilution and high sensitivity for gentamicin detection were selected for cell fusion. Four days before the cell fusion experiment, 100-200µg gentamicin-BSA was added to PBS (0.01 M, pH 7.4) for intraperitoneal injection. Mouse splenocytes were fused with SP2/0 myeloma cells using polyethylene glycol (PEG1450). After fusion, the fused cells were placed in a 96-well cell culture plate and proliferated in HAT medium. 7-10 days after cell fusion, positive hybridoma cells were screened by indirect competition ELISA and subcloned by limiting dilution method.
3. Development and optimization of icCLEIA
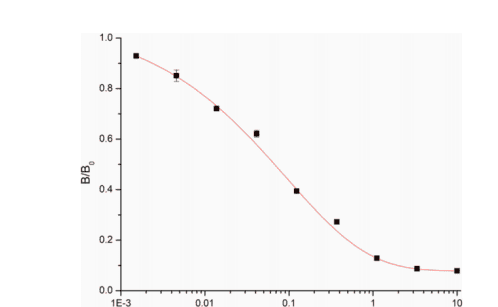
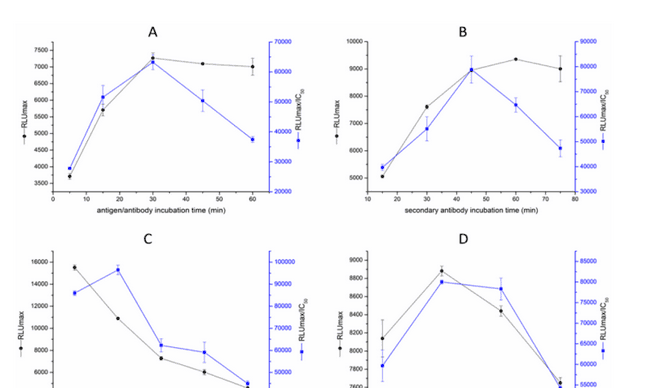
Checkerboard method to detect the concentration of coated antigen and the dilution factor of anti-gentamicin monoclonal antibody. Optimize the immune reaction time, secondary antibody dilution, secondary antibody reaction time and luminescence detection time to improve detection sensitivity. The sensitivity of icCLEIA was evaluated under optimized conditions. The x-axis is the logarithm of gentamicin concentration, B/B0 (B) is the average RLU at the indicated concentration of gentamicin; B0 is the average RLU at zero concentration of gentamicin. Draw the gentamicin standard curve according to B/B0 - logC, and calculate the detection limit (LOD), IC50 and linear range (IC20-IC80) of the gentamicin standard curve through Origin8.5. The results are shown in Figure 1.
As shown in Figure 1. Effect of different working conditions on icCLEIA sensitivity (n = 3). A: Competitive immune reaction time; B: Secondary antibody incubation time; C: Secondary antibody dilution ratio; D: RLU value detection time.
4. Cross-reactivity
As shown in Figure 2. Gentamicin icCLEIA standard curve (n = 3)
As shown in Figure 3. Cross-reactivity of anti-gentamicin monoclonal antibodies and gentamicin analogs
5. Recovery of icCLEIA and its correlation with UPLC-MS/MS analysis
Adopted Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) tested negative for pork and fish samples from local markets. Negative samples were added with gentamicin at concentrations of 0, 0.375, 0.75, and 1.5 μg respectively. Since pork and fish samples contain a variety of proteins and lipids, trichloroacetic acid was used to precipitate proteins and n-hexane was used to extract lipids during sample pretreatment. After sample extraction, the extracts were analyzed using icCLEIA and UPLC-MS/MS. To reduce potential interference from sample components, the extract solution was appropriately diluted with PBST before analysis. In pork samples, the average recovery rate of gentamicin by icCLEIA method is 81% ~ 101%, and the coefficient of variation is 3.7% ~ 6.4%; the average recovery rate of gentamicin by UPLC-MS/MS method The rate is 96% to 106%, and the coefficient of variation is 0.2% to 5.1%. In fish samples, the average recovery rate of icCLEIA is 80% ~ 100%, and the CV value is 0.8% ~ 6.3%; the average recovery rate of UPLC-MS/MS is 100% ~ 105%, and the CV value is 0.8% ~ 3.2 %. The results show that this method can be used as a rapid and efficient screening method for gentamicin residues in animal food.
[Conclusion]
In this study, gentamicin hapten was combined with bovine serum albumin (BSA) and egg cells (OVA) to prepare immunogen and coating antigen. Mouse and cell fusion experiments yielded several high-affinity gentamicin-resistant positive hybridoma cells. Ascites monoclonal antibodies were prepared using specific hybridoma-positive cells 40H6 as raw materials and purified by affinity chromatography. Based on the purified ascites monoclonal antibody, a highly sensitive icCLEIA for gentamicin animal tissue detection was established, with an IC50 of 0.067 ng/mL, LOD of 0.002 ng/mL, and cross-reactivity with structural analogues <0.01% . The recovery rate of gentamicin in pork and fish samples was 80 to 101%, and the coefficient of variation was less than 6.4%. Compared with previously reported gentamicin detection methods, the icCLEIA developed in this study has higher sensitivity and specificity. The reliability and accuracy of the icCLEIA method were verified by comparison with UPLC-MS/MS. Therefore, the icCLEIA method established in this study can be used as a powerful tool for routine screening of gentamicin residues in animal foods.
 扫一扫微信交流
扫一扫微信交流
发布评论