It is not advisable to keep cats during pregnancy because people are afraid of being infected with toxoplasmosis in cats. Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii. It is a common parasite. Cats are its main host. It is a globally distributed zoonotic infectious disease.
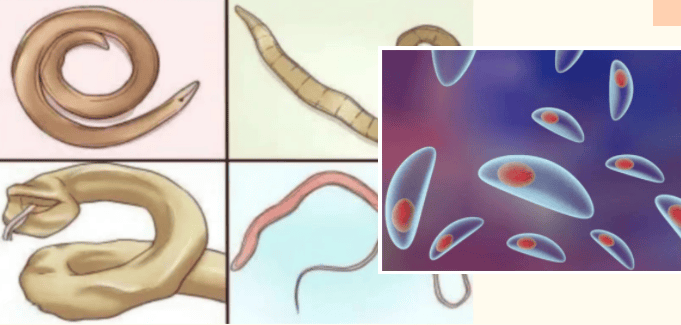
The transmission method and harm of Toxoplasma gondii
Toxoplasma gondii can be transmitted through cat feces. If pregnant women are accidentally infected when cleaning cat litter, Toxoplasma gondii Pathogens can be transmitted to the fetus through the placenta. If infected with Toxoplasma gondii in the first 3 months of pregnancy, it may cause severe damage to the fetal central nervous system and eventually lead to fetal death. If infected with Toxoplasma gondii during the third trimester of pregnancy, it may cause hydrocephalus, mental retardation, psychomotor retardation, blindness and brain calcification in the baby. However, infection with Toxoplasma gondii is most common in the third trimester of pregnancy and can lead to retinochoroiditis and other eye damage in the baby. Damage to the central nervous system and latent asymptomatic infection can eventually lead to disease.
Toxoplasma gondii testing items
Toxoplasma gondii is the first letter T in TORCH, a test related to eugenics and postnatal care. TORCH is the abbreviation of the English name of a group of pathogenic microorganisms, where T (Toxoplasma gondii, Toxo) represents Toxoplasma gondii, R (rubellavirus, RV) represents rubella virus, C (cytomegalovirus, CMV) represents cytomegalovirus, and H ( herpes simplex virus (HSV) stands for herpes simplex virus, and 0 (others) refers to other related viruses such as Epstein-Barr virus, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and human parvovirus B19. Pregnant women infected with these pathogens in early pregnancy may cause premature delivery, miscarriage, intrauterine growth retardation, malformation, stillbirth and neonatal death.
Identification of recent and past infections with Toxoplasma gondii
After human beings are infected with Toxoplasma gondii, protection can generally be produced immunity. They also appear in the order of specific IgM first and then IgG antibodies. Specific IgG antibodies reach their peak 2 to 5 months after the onset of clinical symptoms. At the same time, as the immune response progresses, antibody affinity gradually increases. In recent infections, the avidity of IgG antibodies is low, whereas in past infections, the avidity of IgG antibodies is high. Therefore, antibody avidity measurement can be used to distinguish recent and past infections.
 扫一扫微信交流
扫一扫微信交流
发布评论